In this article, we are going to learn about the 22 basic ssh commands that you should know about. By reviewing this, you will understand how to navigate, manage and command your terminal, VPS or server through the command line.
How to Access Remote Server or Terminal :
To start for the command line, make sure that you have access to a remote server or shell prompt. Also, one can demand ssh enable through chat or ticket if you own shared, reseller or vps hosting with Hostpoco. You can then find an option named Terminal under hosting cpanel, where you can use these basic commands.
SSH stands for Secure Shell, it’s a type of protocol used to securely connect to a remote server/system.
Steps to access your remote server:
There are two well-known and recommended methods to make ssh connection. Using an SSH client like Putty. It requires you to enter the server’s IP and the port number into the corresponding fields.
Using Terminal Shell: This is the option available under hosting Cpanel which you will be able to see once your hosting provider enables ssh access for your account.
You will need to write details under the destination section of putty along with the port number:
ssh user@serverip or hostname
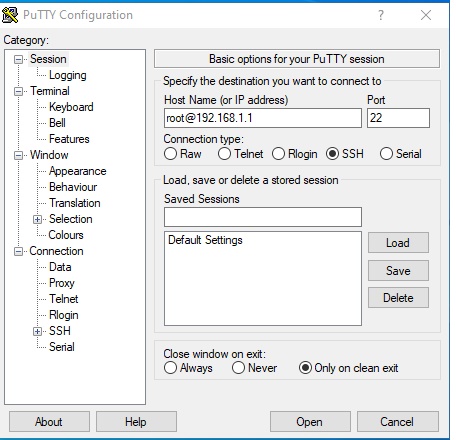
Remember to replace ssh “root” with your real username and ssh “192.168.1.1” with your server’s dedicated or shared IP address.
Make sure that you have filled the correct details and then click on open. Once you click the Open button on PuTTY or the accessed the terminal option under Cpanel, you will be prompted for a user/shell password. If you are making ssh connection first time on the server then you might get a warning message, telling you that the server is not recognized. Just click on Yes to continue.
Done. Now you’re connected to the server and can start executing SSH commands from your end.
List of Basic SSH Commands
Now we will go through popular SSH commands and learn about using them.
Here is the quick look of the basic SSH commands which we will cover.
| SSH Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
ls | Show directory contents (list the names of files). |
cd | Change Directory. |
mkdir | Create a new folder (directory). |
touch | Create a new file. |
rm | Remove a file. |
cat | Show contents of a file. |
pwd | Show current directory (full path to where you are right now). |
cp | Copy file/folder. |
mv | Move file/folder. |
grep | Search for a specific phrase in file/lines. |
find | Search files and directories. |
vi/nano | Text editors. |
| chmod | Help to change the permission of the files or directories |
| chown | Help to change ownership of the files or directories |
| zip -r | zip -r directory.zip directory name helps to make a zip of directory |
| unzip | unzip filename helps to unzip directory |
| mysqldump | Helps to take backup of database |
history | Show last 50 used commands. |
clear | Clear the terminal screen. |
tar | Create & Unpack compressed archives. |
wget | Download files from the internet. |
du | Get actual file size. |
ls command
This command is useful to list the contents available under the directory
Also available the below options to get more info
-l : ls -l displays the details of the files, such as size, modified date and time, the owner, and the permissions.
-a : ls -a shows hidden files and directories
cd command
cd (Change Directory) is the command that use to jump between directories. This is a simple command, just type cd followed by the name of the directory:
cd [directory]
eg : cd home , cd testdirectory
To go back one level reverse, you can simply enter “..” (two dots) after cd command:
cd ../..
Enter this command to get in-home directory again.
mkdir command
This command is useful to create new directory
mkdir [folder name]
Assume that you want to create a new folder named “mydata”. You will need to type:
mkdir mydata
touch command
one can easily create new file using this command, it can be with extension or without extension. It can create files without any extension too
touch [file name]
If you want to create a .txt file named “testfile”, this is what you need to write:
touch testfile.txt.
rm command
rm command helps to remove a chosen file or directory. To delete a file, enter:
rm [file name]
For instance, if you want to remove testfile.txt, simply execute:
rm testfile.txt
To delete a directory, you need to use the -r (recursive)option to remove all the files and subfolders inside it:
rm -r home3/hostpoco/mydat
cat command
This command is very useful to view contents from the file
cat [file name]
This also allows you to create a new file by merging multiple files. Eg:
cat info.txt info2.txt > infomerge.txt
This execution will help to merge the content of info.txt and info2.txt into infomerge.txt
pwd command
pwd is a command that prints the full path of your working directory. Eg:
home/user/public_html
It’s handy if you want to get the exact path in case you need to update your provider for some work
cp command
This ssh type of command is helpful to copy files and folders.
cp [options] [source] [destination]
[source] should be the file or folder you want to copy and [destination] is the duplicate.
Let’s assume that you have mydata.txt in your working directory, and you want to make a copy of it. It should work like below way:
cp mydata.txt mydata2.txt
Also if you want to make a copy in a different folder, run the below command:
cp /home/hostpoco/mydata.txt /home/testuser
mv command
This command works in a similar way to cp. However, mv command will move the file or folder instead of copying it. This is the syntax:
mv [source] [destination]
grep command
grep command is for searching purposes, looks for a given string in files. For example:
grep ‘line’ info.txt
The above command would search for ‘line’ in a file named “info.txt”.
find command
This command is useful to search for a file/files that meet with the format (name, size, file type, etc). The basic syntax is as below:
find [starting directory] [options] [search term]
[starting directory] is where you would like to start your search process. There are three main choices:
/ (slash) — search the whole system
. (dot) — search the working directory
~ (tilde) — search the home directory
Additional arguments :
-name — look for files based on their names
-user — search for files that belong to a given user
-size — look for files based on their sizes
[search term] is the keyword or number that you use to search for files.
Take a look at this example:
find . -name “index”
This command will return any files that have the word “index” on their names. And since we use “.” (dot), the command will only search the working directory.
vi/nano command
Vi and Nano are the popular text editors from where you can view, modify your files. You can simply fire the below type of command if you wish to modify any file:
vi [yourfilename]
or
nano [yourfilename]
chmod command
This command type is use to change the permission of file or folder. Generally its not useful for shared hosting but useful in case you have vps or dedicated server. Eg :
chmod 644 filename ; chmod 755 filename
here 644 mean read and write access
and 755 read, write and executable access
chown command
This command is use to change ownership of file or directory. This also mostly used on vps or dedicated server only
zip command
This command is used to make zip file of the contents or directories. eg :
zip -r directoryname.zip directoryname
unzip command
This command is used to unzip any zip file and syntax should be as below :
unzip directoryname.zip
mysqldump command
This command is useful to generate backup of your database
mysqldump -h [SERVER] -u [USER NAME] -p [DATABAS]> dumpfil.sql
This result into exports of your database and saves it as “dumpfil.sql”. The brief of arguments used in above command are as below :
-h : hostname of database server
-u : username of database user
-p : password of database
history Command
This command is useful to display the last used commands. You can enter a number to limit the displayed results. eg:
history 10
This will show you the last 10 used commands
clear command
This command helps to clears all text from the terminal screen
tar Command
tar is a famous SSH command that creates or extracts .tar.gz files. It is very popular because most third-party software binaries are in the .tar.gz format also best options for backup creation and extraction
To compress a folder in .tar.gz format, use the below command:
tar cvzf archivedfile.tar.gz /path/to/directory
To uncompress a .tar.gz file, enter this command:
tar xvzf archivedfile.tar.gz
The both above commands use different four-character options — cvzf and xvzf. Each letter represents a specific instruction as below:
x used to extract files
c used to create an archive
v stands for verbose.. use to display all file names that are processed by the command.
z used to uncompress the archive file
f use to define name of the archive
wget command
This is the command used to download files from the internet. For example, you wish to fetch downloadable backup from the website then you can use below syntax
wget http://yourfileurl/sitebackup.tar
If you want to download multiple files then you need to put URLs into a file and use the -i option.
du command
You can use du ie disk usage command to view exact size of files, directories and more info
du [folder path]
In most of the cases vps and dedicated server always have shell access but not for shared hosting. Limited hosting providers are offering shell or terminal access, you can try Hostpoco hosting services if you wish to get shell access.
Summary
Getting familiar with ssh commands is a crucial task but essential for managing Linux server, vps or hosting. It is the most effective way to navigate through your system and modify files or directories.
Glad to see, that you have learned about basic ssh commands. Its useful for handling your server related tasks. Please contact us for more queries.
